Example case studies from our radiology and imaging study days..
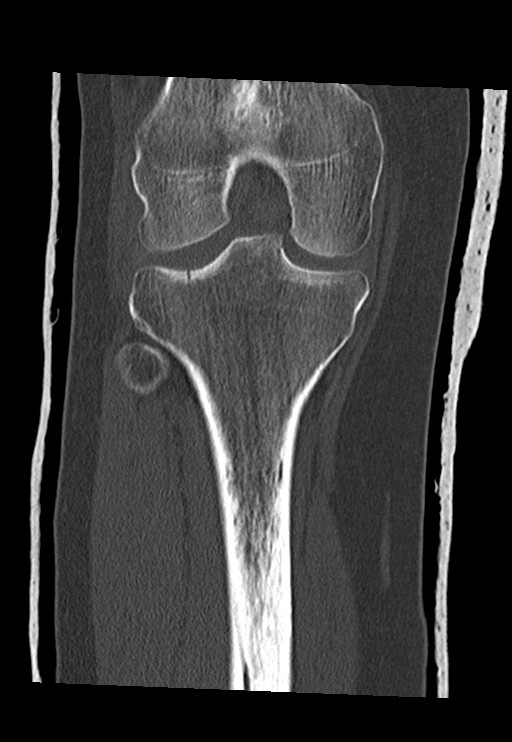
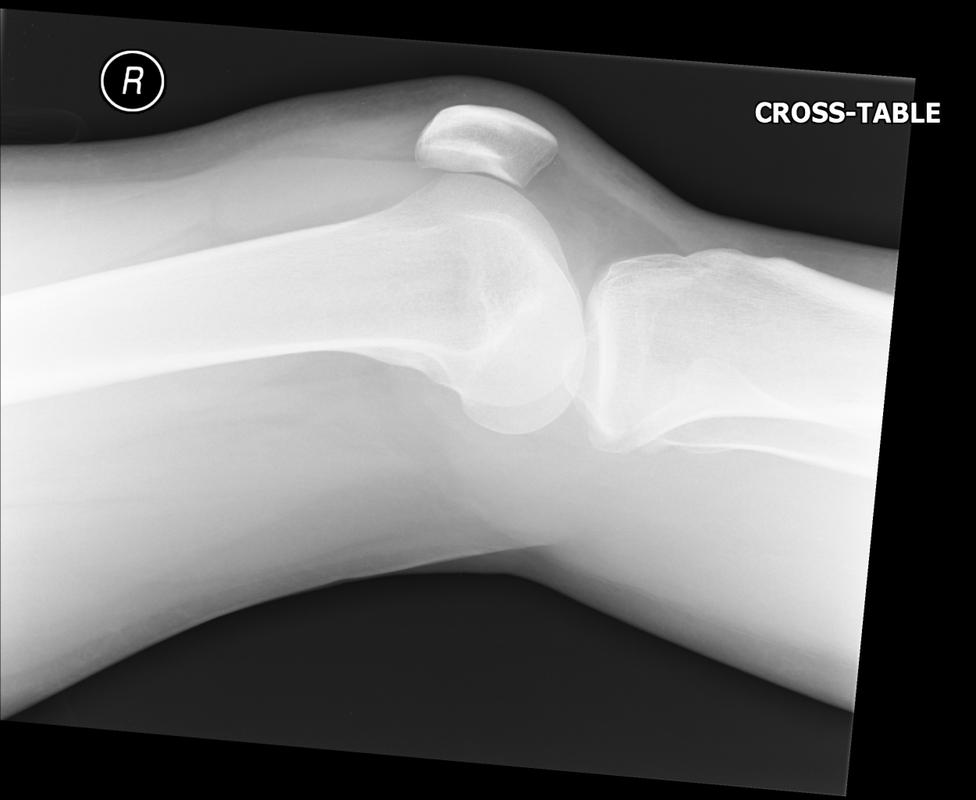
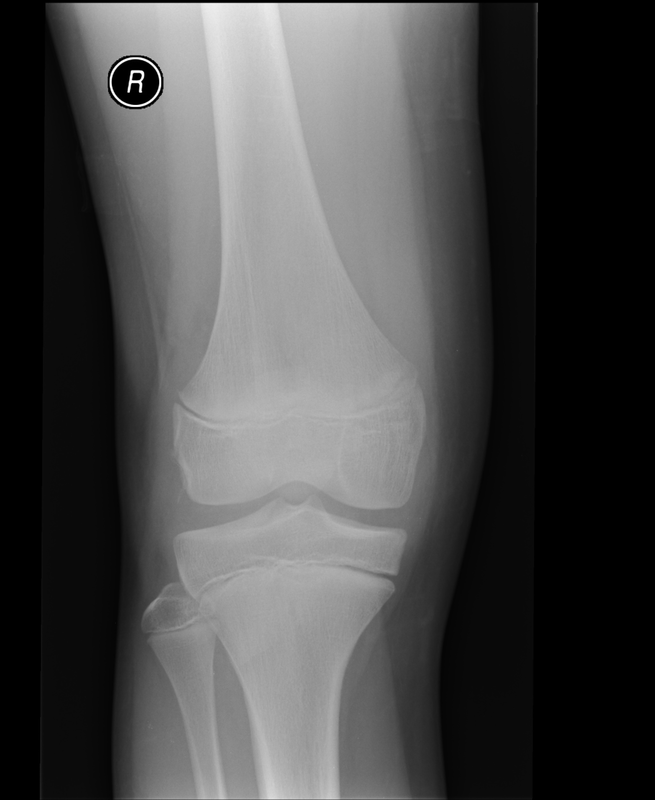
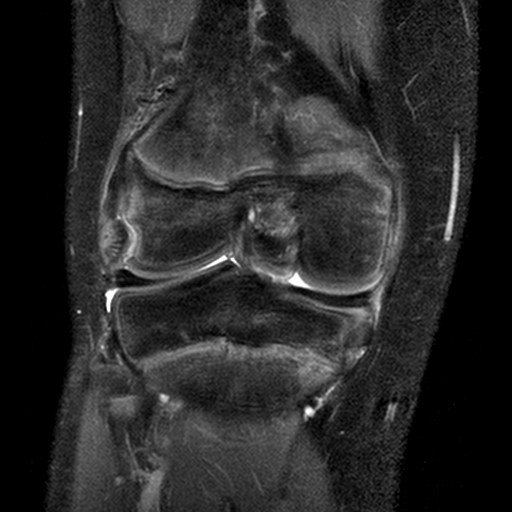
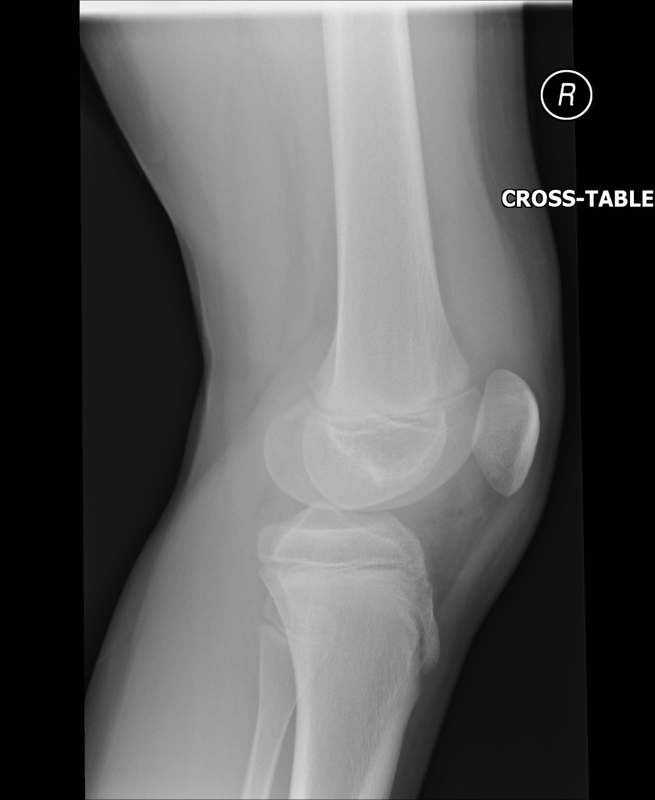
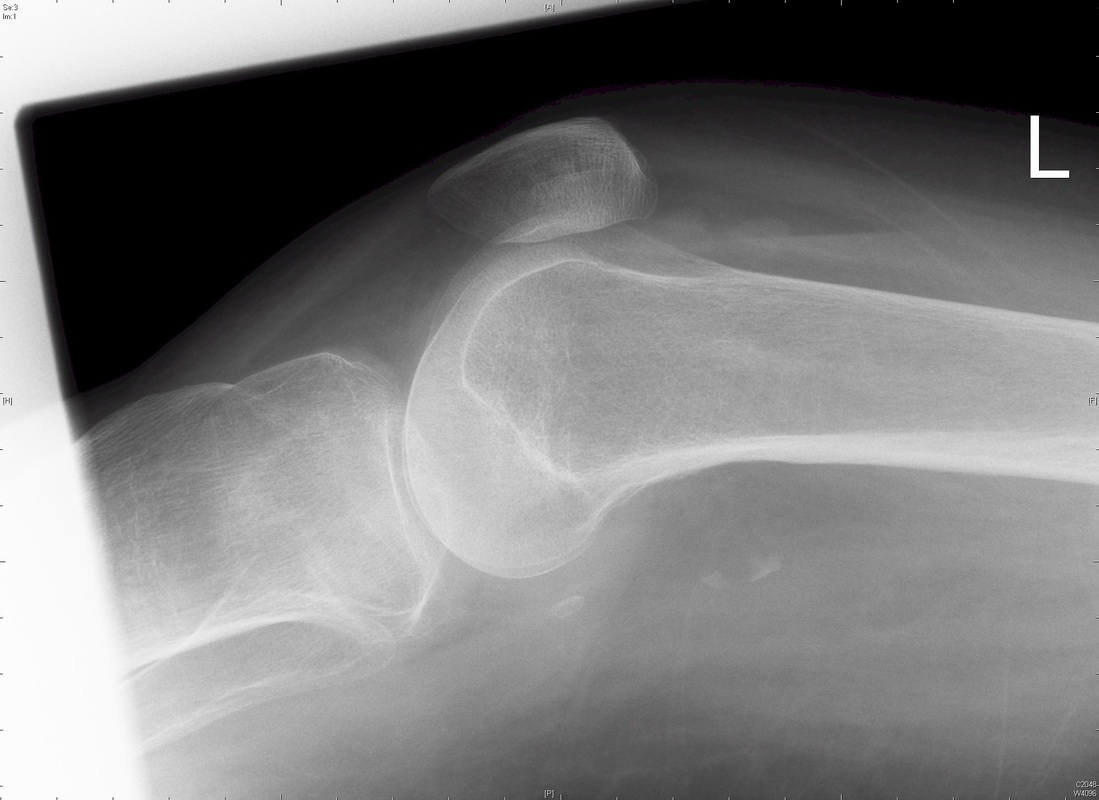
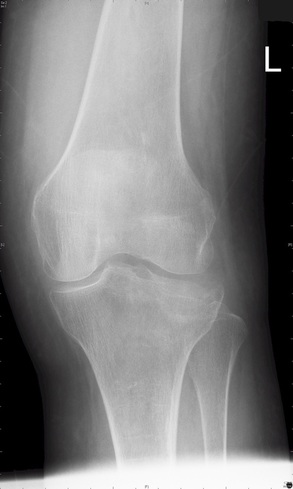
Lipohaemarthrosis
Technique: Plain film – AP and lateral projections
Technique: Plain film – AP and lateral projections
|
Findings: Depressed or impacted fracture of the right lateral tibial plateau with a fat-fluid level evident on the lateral plain radiograph (Lipohaemarthrosis). This occurs in intra-articular fractures due to escape of fat and blood from the bone marrow into the joint space forming a fat-fluid level best appreciated on the lateral radiograph. This is most frequently seen in the knee, associated with a tibial plateau fracture or distal femoral fracture. Tibial plateau fractures are classified using the Schatzker classification system which divides fractures into six subtypes. The above example is a Schatzker I fracture.
|
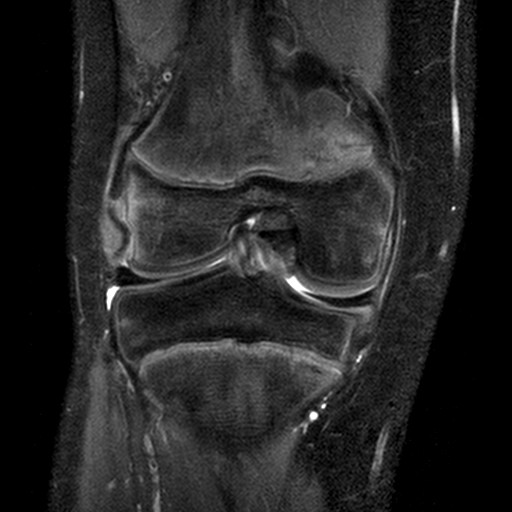
A rare isolated injury
Technique: Plain film – AP and Lateral radiographs and STIR Coronal MRI.
Technique: Plain film – AP and Lateral radiographs and STIR Coronal MRI.
|
Findings: Isolated popliteus tendon avulsion fracture in a paediatric patient. A curvilinear fracture of bone is demonstrated parallel to the lateral femoral condyle representing a bony avulsion fracture. On the MRI, there is high signal within the popliteus tendon and confirmation of the avulsion fracture.
|
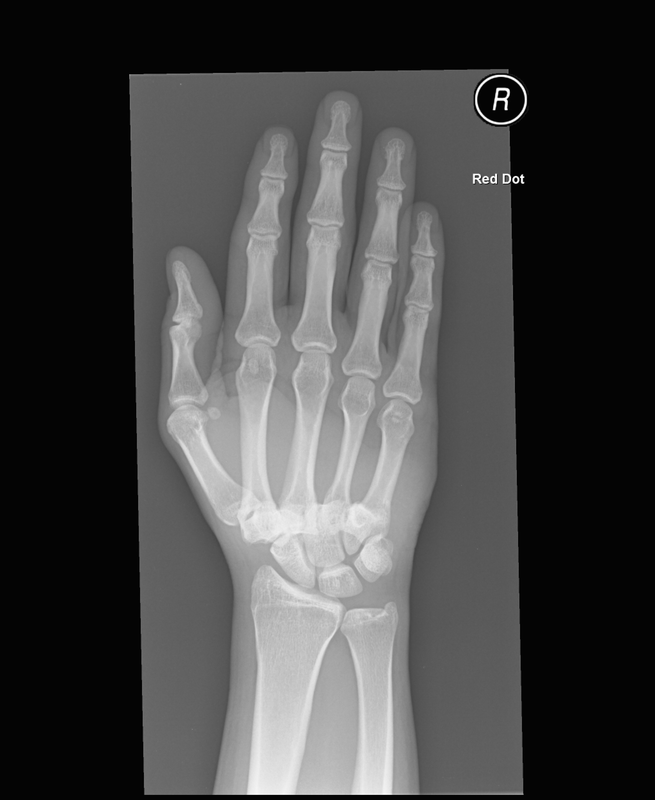
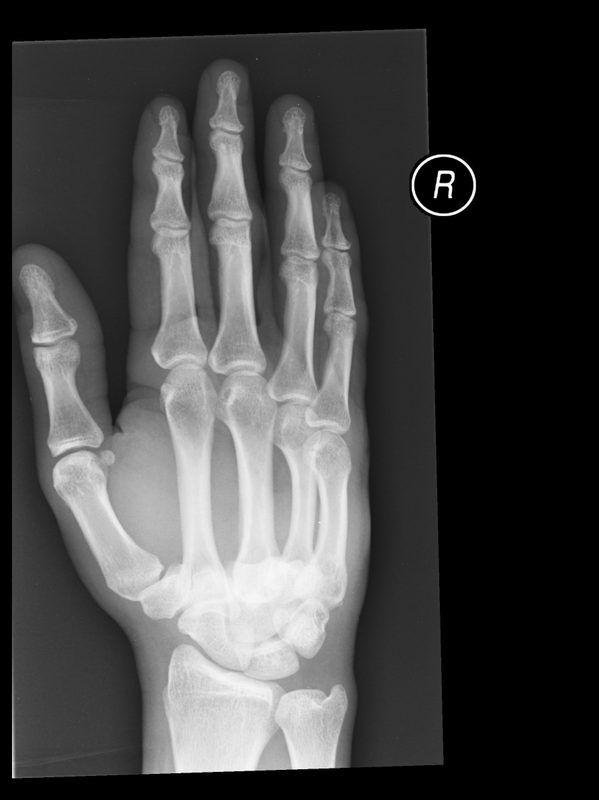
Punch injury followed by a fall
Technique: Plain film – AP and oblique radiographs
Technique: Plain film – AP and oblique radiographs
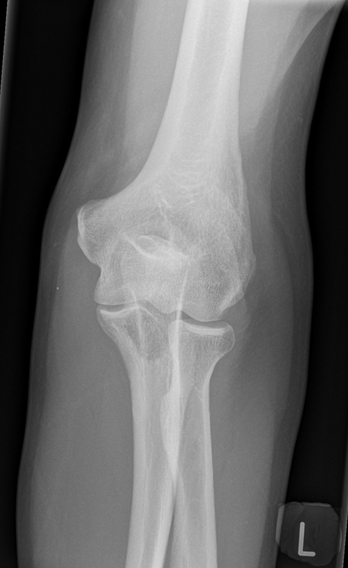
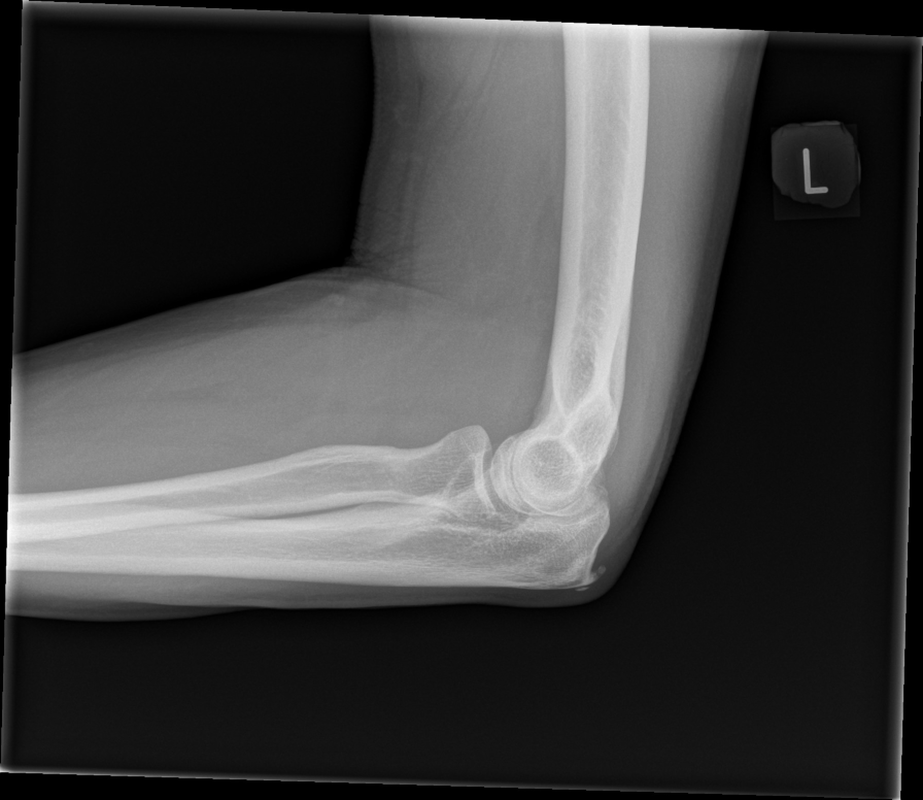
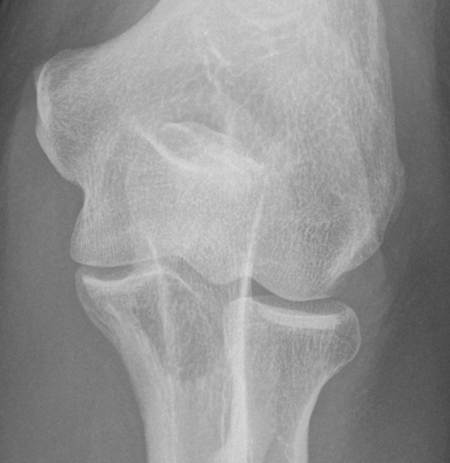
Sudden onset of elbow pain
Technique: Plain radiographs – AP and Lateral projections
Technique: Plain radiographs – AP and Lateral projections
|
Findings: No soft tissue swelling or joint effusion. Normal elbow alignment. Degenerative enthesophytes at the triceps tendon insertion on the olecranon. However, there is also a relatively well defined low density (lytic) lesion within the ulnar best appreciated on the AP-view. This proved to be a renal cancer metastasis.
|
Painful forefoot
Technique: Plain film – AP projection
Technique: Plain film – AP projection
Findings: There is flattening of the 2nd metatarsal head with widening of the 2nd metacarpophalangeal joint (MCPJ). The appearances are consistent with osteochrondrosis of the metatarsal head and a condition called Freiberg’s Disease. This is most common in women aged between 10-18yrs with high heeled shoes being postulated as one causative factor.
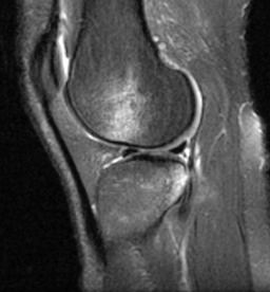
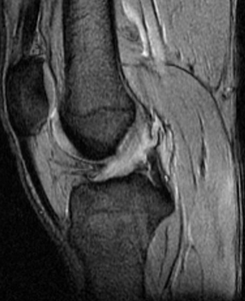
Kissing Contusions:
Technique: Sagittal T2 Fat Saturation MRI
Technique: Sagittal T2 Fat Saturation MRI
Findings:
Kissing contusions on the anterior lateral femoral condyle - posterior tibial plateau. Bone marrow oedema (bone bruise) represents the footprint for the mechanism of injury. In this case, there is an underlying anterior cruciate ligament rupture following a hyperextension and rotation mechanism of injury.
Kissing contusions on the anterior lateral femoral condyle - posterior tibial plateau. Bone marrow oedema (bone bruise) represents the footprint for the mechanism of injury. In this case, there is an underlying anterior cruciate ligament rupture following a hyperextension and rotation mechanism of injury.
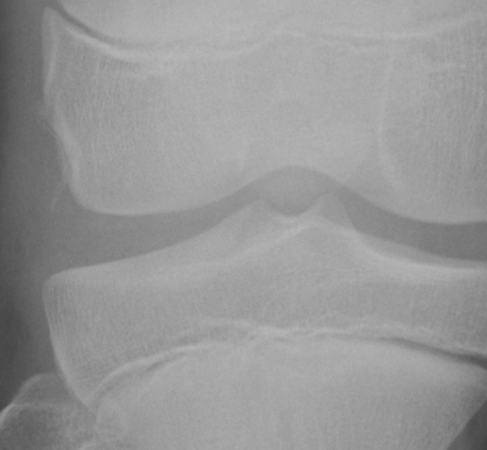
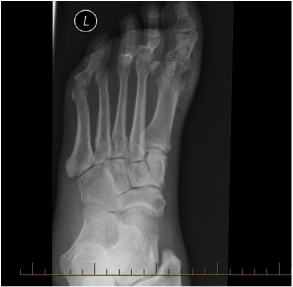
Painful big toe
Technique: Plain radiograph Foot
Technique: Plain radiograph Foot
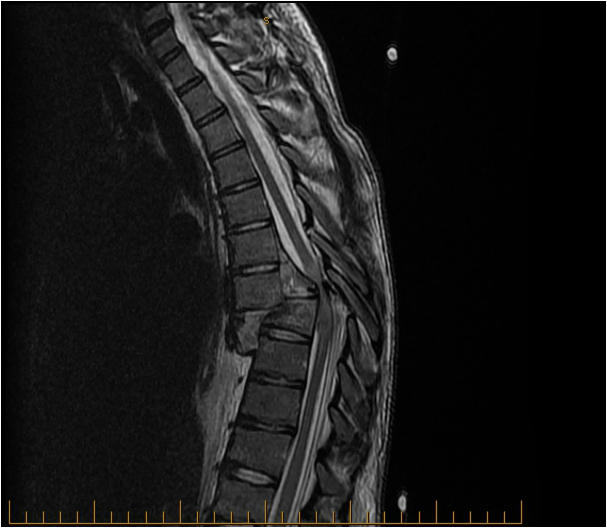
Paraplegia with sensory level at T7/8
Technique: T2 Sagittal MRI
Technique: T2 Sagittal MRI
Findings: Acute T7/T8 fracture-dislocation. Severe central canal stenosis with thoracic spinal cord compression and cord oedema due to a combination of the fracture-dislocation, epidural haematoma and displaced bone fragments within the central spinal canal.
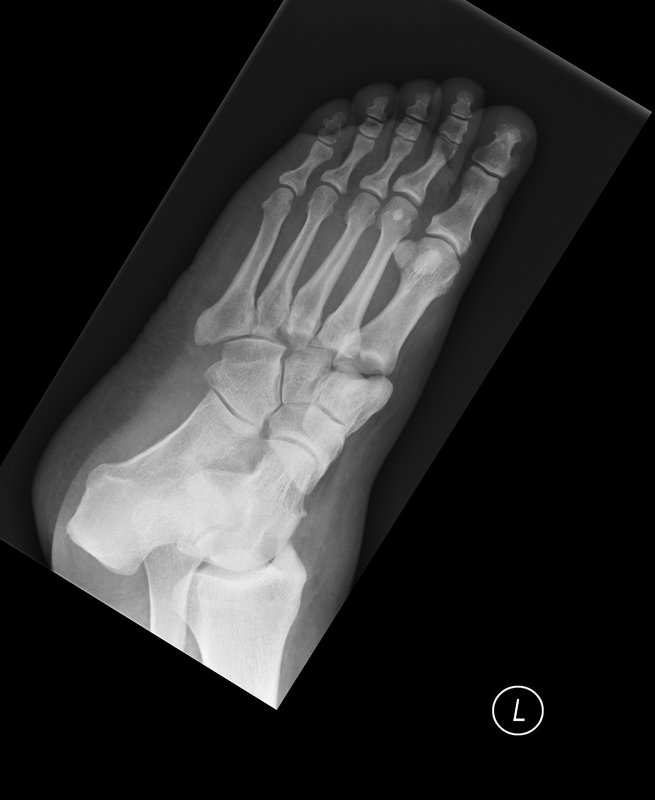
Fall, painful foot and non-weightbearing
Technique: Foot plain radiographs
Fall, painful foot and non-weightbearing
Technique: Foot plain radiographs
Finding: Homolateral Lisfranc fracture-dislocation. Lateral dislocation of the 1st -5th metatarsals relative to the tarsus following rupture of the Lisfranc ligament the medial cuneiform to the 2ndmetatarsal base on the plantar aspect of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint.
Findings: Lipohaemarthrosis with a depressed lateral tibial plateau fracture. Lipohaemarthrosis results from an intra-articular fracture with escape of fat and blood from the bone marrow into the joint, and is most frequently seen in the knee, associated with a tibial plateau fracture or distal femoral fracture.
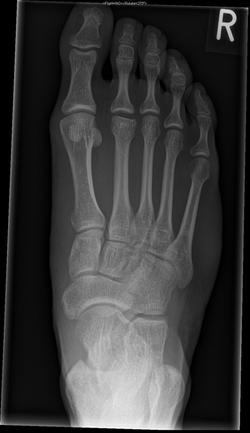
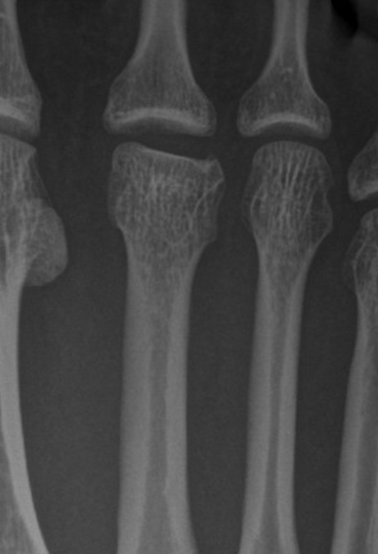
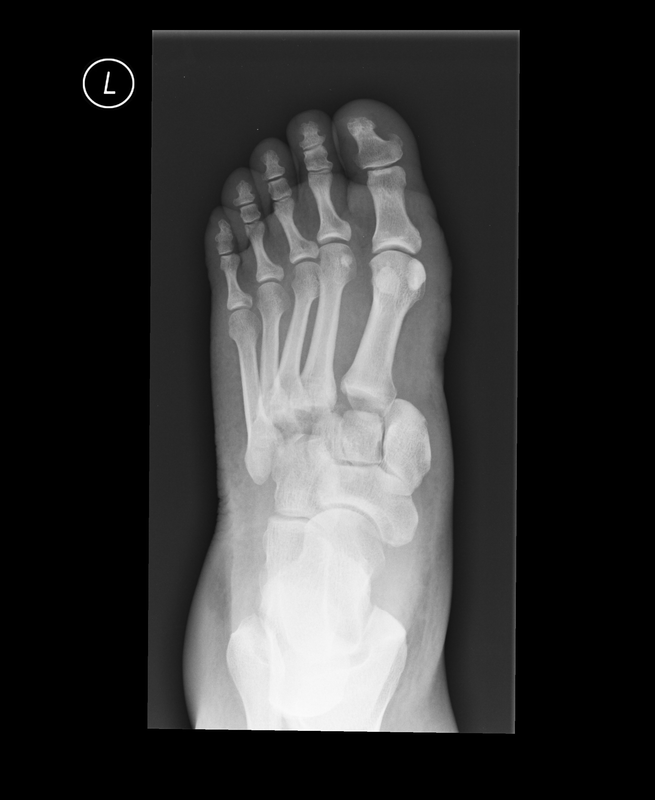
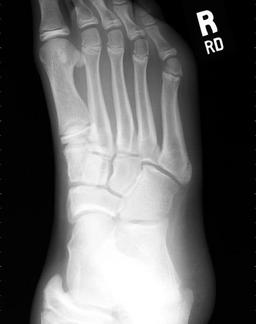
Painful foot
Technique: Oblique radiograph of the foot
Painful foot
Technique: Oblique radiograph of the foot
Findings: Normal fusing apophysis at the base of the 5th metatarsal in a skeletally immature patient. No acute fracture or dislocation.
MSK Radiology and Imaging Course
2 days with a highly experienced Registrar Radiologist exploring essential Musculoskeletal Radiology for Therapists and Allied Health Professionals. This course will assist delegates in making clinically appropriate requests for imaging and to apply a systematic approach when interpreting images. With interactive sessions, ‘packets’ of normal/abnormal cases and essential tips & tricks delegates will develop their diagnostic skills and gain valuable insights into how to get the most from a Radiology service. Questioning and debate are actively encouraged in this interactive course which is suitable for practitioners with experience of radiology or those wishing to get their first taste.
Learning Objectives:
- Delegates will gain an understanding of clinically relevant physics in radiological imaging.
- Delegates will gain knowledge of the principles of IRMER and the essentials of radiation protection.
- Delegates will learn a systematic approach to trauma musculoskeletal radiographs and gain an insight into more advanced radiological investigations such as CT and MRI.
- Delegates will develop their diagnostic skills with the use of multiple ‘packets’ of both normal and abnormal radiographs.
|
Course Outline:
Day 1:
|
Day 2:
|
Tutor:
Dr Richard James Bsc (Hons) MBBCh (Hons) FRCR
Radiology Registrar at Southmead Hospital, North Bristol NHS Trust.
Hugely experienced in all aspects of Clinical Radiology with subspecialty training in paediatrics, trauma, musculoskeletal, neuroradiology, chest and GI radiology, involving all imaging modalities such as plain radiographs, ultrasound, CT, MRI and nuclear medicine. Richard is currently a final year Radiology Registrar with pending appointment to a Consultant Radiologist post in 2016/17.
Date: April 23rd and 24th 2016
Location: Central Bath
Course fee: £99 for 1 day £180 for the weekend.
To book a place: E-mail [email protected] or call 07917327322
Dr Richard James Bsc (Hons) MBBCh (Hons) FRCR
Radiology Registrar at Southmead Hospital, North Bristol NHS Trust.
Hugely experienced in all aspects of Clinical Radiology with subspecialty training in paediatrics, trauma, musculoskeletal, neuroradiology, chest and GI radiology, involving all imaging modalities such as plain radiographs, ultrasound, CT, MRI and nuclear medicine. Richard is currently a final year Radiology Registrar with pending appointment to a Consultant Radiologist post in 2016/17.
Date: April 23rd and 24th 2016
Location: Central Bath
Course fee: £99 for 1 day £180 for the weekend.
To book a place: E-mail [email protected] or call 07917327322